Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a serious threat to human life that includes peripheral artery disease, coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebral artery disease. In fact, most CVD is caused by blood clots and CAD has become one of the most common causes of death in China. Myocardial biomarkers are biochemical indicators of cardiac disease and help in the early diagnosis, clinical stratification and prognostic assessment of myocardial injury, especially acute myocardial infarction in coronary artery disease.
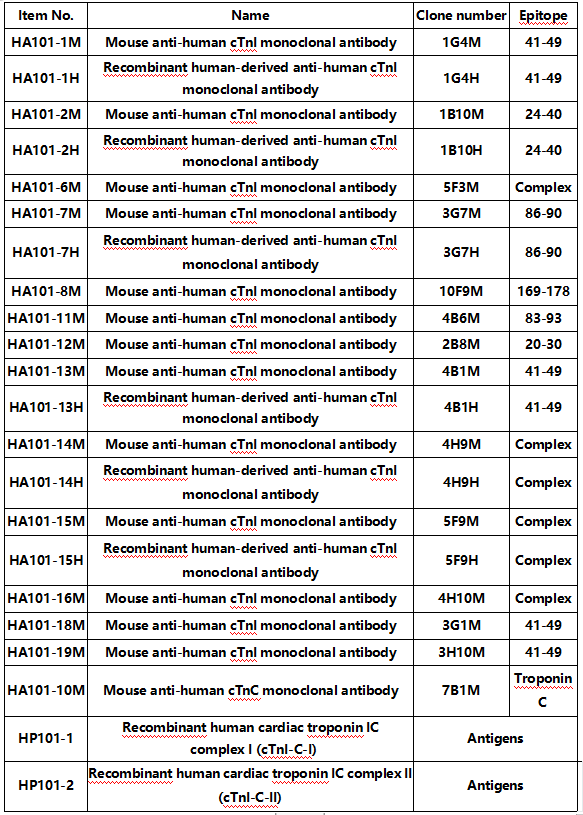
01 Cardiac troponin I (cTnI)
cTnI is the most sensitive and specific marker of myocardial cell injury and is recognized as the primary biochemical marker for rapid diagnosis of AMI and ACS as well as for assisting in the risk stratification of ACS and reflecting its prognosis. So it is therefore considered the gold standard biomarker for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. In addition, the next generation high-sensitivity cTnI assay is useful for long-term risk classification in different patient groups, including patients with heart failure or stable coronary artery disease.
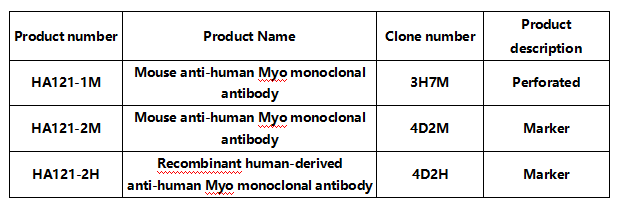
02 Myoglobin(Myo)
Myoglobin is the best early marker used for myocardial injury. Because it is a small molecule, it can be rapidly introduced into the blood during acute myocardial infarction (AMI), so within 1.5 to 6 h of AMI, the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction can be made by dynamic testing of the second serum myoglobin level. If the second test value is significantly higher than the first test value, it has a very high positive predictive value; if there is no difference between the second dynamic test values, it has a 100% negative predictive value and excludes the possibility of acute myocardial infarction. It should be noted, however, that myoglobin may be elevated in severe shock, severe extensive trauma, end-stage renal insufficiency, myocarditis, and acute infection.
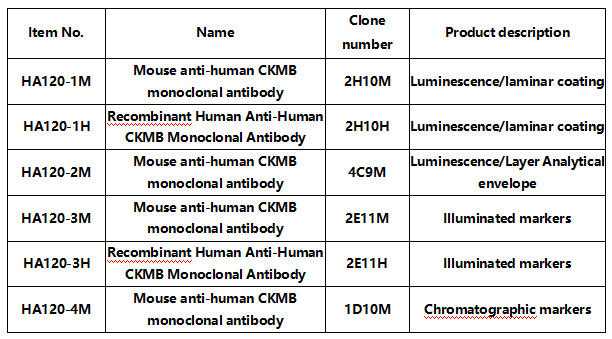
03 Creatine kinase isoenzyme(CK-MB)
CK-MB is found mainly in the outer plasma layer of cardiomyocytes and has been widely used for many years since the 1970s as the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of AMI due to its high sensitivity and specificity. CK-MB appears earlier than traditional enzymatic indicators. CK-MB is the best early indicator of recanalization, and the peak of CK-MB is significantly earlier in thrombolytic recanalization, which is valuable for determining revascularization.
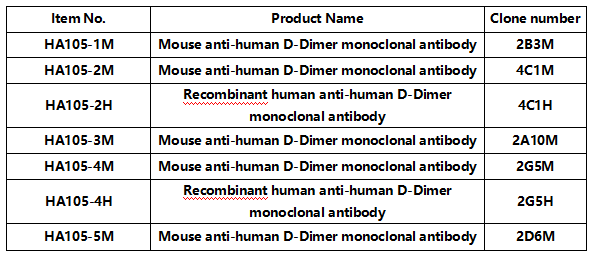
04 D-Dimer(D-Dimer)
D-dimer is a small molecule dimer produced by the action of fibrinolytic enzymes on cross-linked fibrin eggs, and its increase reflects the secondary enhancement of fibrinolysis. As a marker of hypercoagulability and hyperfibrinolysis in vivo, it is important for the diagnosis, efficacy observation and prognosis of thrombotic diseases and the hypercoagulable state of blood.
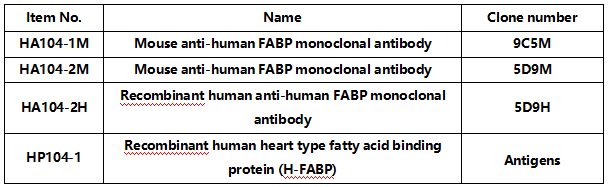
05 Heart-type fatty acid binding protein(H-FABP)
Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) is a novel small cytoplasmic protein that is enriched in the heart. It is also specifically present in cardiac myocytes. Under normal physiological conditions, H-FABP does not appear in plasma or tissue fluid and is released into the blood early in myocardial injury. It is one of the earliest markers released into the circulation during myocardial injury, and starts to rise 1-3 hours after the onset of ACS, peaks at 6-8 hours, and returns to normal at 12-24 hours. It has its own advantages as an early marker of myocardial injury.
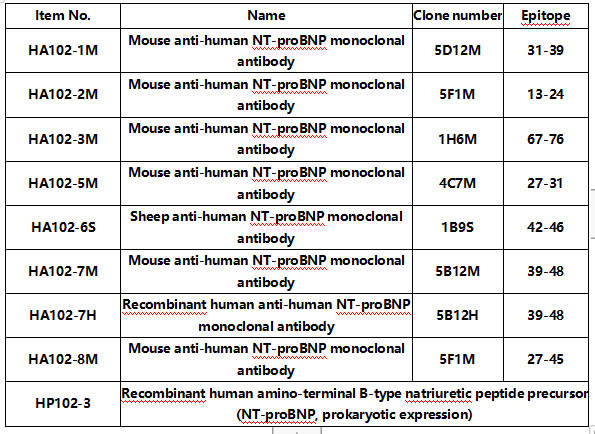
06 Amino-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide precursor(NT-proBNP)
NT-proBNP and BNP are of the same origin and both precursors are the hormone proBNP,NT-proBNP has a molecular weight of 23.9 kD and is produced by cardiac myocytes. The cardiomyocytes first synthesize the B-type natriuretic peptide precursor containing 134 amino acid pairs, which is subsequently cleaved into NT-proBNP and the C-terminal peptide BNP by the action of a series of endonucleases. NT-proBNP is a biochemical index for the diagnosis of heart failure and has promising potential for the assessment of hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy and the prognostic evaluation of acute coronary syndromes.
07 Soluble ST-2
ST-2 is used as a biomarker for risk stratification as well as prognostic assessment in patients with heart failure (HF). Unlike many other cardiac markers, ST-2 levels can change rapidly as a patient's condition changes. This means that ST-2 can help clinicians respond more quickly. Elevated ST-2 levels (>35ng/ml) in patients with acute and chronic heart failure are highly correlated with the severity of heart failure and can be used for readmission and mortality prediction. A large body of literature shows that ST2 is an independent predictor of all-cause cardiac mortality, and that ST-2 may also provide prognostic information complementary to NT-proBNP (BNP) and ultrasensitive troponin T.

References:
(1) Christenson, R., 2007. Evidence-based laboratory medicine - a guide for critical evaluation of in vitro laboratory testing. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry: International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 44(2).
(2) Contemporary medicine, Beijing: China Medical and Health International Exchange Promotion Association, 1994. (1009-4393).










